‘It’s Just So Fantastic’: Wolverine Family Seen At Mount Rainier, No Signs Yet Of Cyclops Or Beast
READ ON
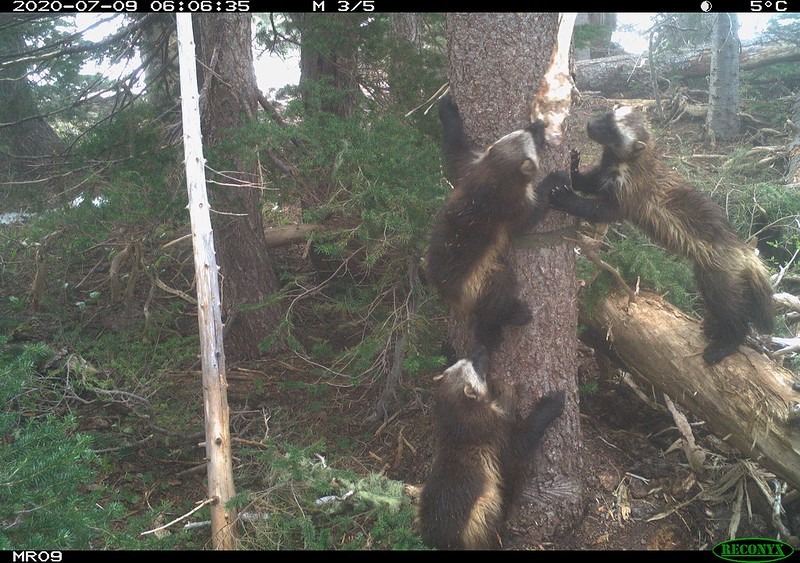
Conservationists are “cautiously optimistic” after discovering a mother wolverine and her kits at Mount Rainier National Park. It’s the first time a family of wolverines has called the park home in more than 100 years.
Wolverines, which look like small bears with bushy tails, are candidates for being listed as threatened species in Washington. Most live in the North Cascades.
Biologists hope wolverines can establish a home range south of Interstate-90. They’ve spotted a handful of the carnivores in the past several years, and are hoping new wildlife bridges and underpasses will help with their movements south.
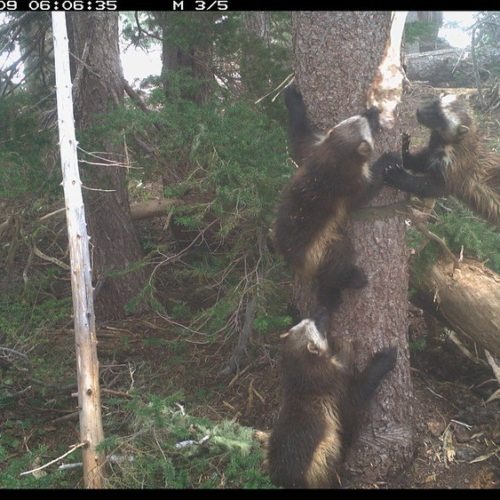
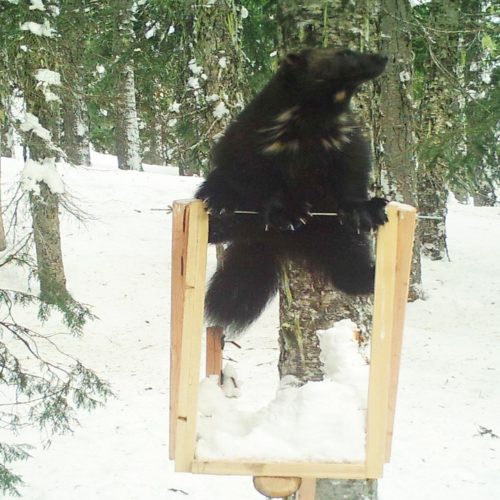
Wildlife watchers first noticed a potential mother wolverine on special cameras set up at Mount Rainier. The kits were spotted several months later. The cameras are able to catch distinct patterns on the wolverine’s chest. That’s one way groups can track their movements. Right now the park has six cameras to monitor for wolverines.
Hikers confirmed the family was still alive this month when they captured the wolverine family on video.
Wolverines Return to Mount Rainier National Park After More Than 100 Years, News Release: https://t.co/qmCkTDsFAU
Video of three wolverines at the end of a snowfield then running through a meadow into a forest. Credit: Travis Harris -kl pic.twitter.com/ALwJoAOmTG— MountRainierNPS (@MountRainierNPS) August 20, 2020
Jocelyn Akins, with the Cascades Carnivore Project, said wolverines depend on remote, snowy, high-elevation habitat that is threatened by climate change.
“Wolverine reproduction in the south Cascades is an incredible indicator of the intactness of our wilderness areas, Akins said. “It’s just so fantastic that a carnivore that was once historically on the landscape is back and reproducing.”
Because wolverines need such specific habitat, their presence can be a sign of the health of the ecosystem.
But there still are a lot of challenges to the wolverine population persisting in Washington’s south Cascades.
Climate change is a big concern because it will melt the snowy areas where they need to burrow into snowpack to create dens. There are also long distances for the carnivores to travel to make it south of I-90.
“If we just have this small family of individuals, it’s going to be a very small inbred population,” Akins said.
In Oregon, wolverines are listed as a threatened species. A few years ago, a wolverine was spotted in the Wallowa Mountains in the northeastern part of the state.
At Mount Rainier, officials are asking people to not disturb the wolverines or announce their location, if you happen to see them.
But they are enlisting help from backcountry visitors. For one, visitors can report sightings to the Mount Rainier online wildlife observations database or the Cascades Wolverine Project.
Park ecologist Tara Chestnut says wolverines pose no serious risk to people and are shy and elusive. So if you’re lucky enough to spot one – and can maintain a safe distance – backcountry observations are very important.
“Visitors have lots they can contribute to wolverine and carnivore conservation in the Cascade range,” Chestnut said. “Backcountry enthusiasts are very important to monitoring species.”
The park is working with the Cascades Carnivore Project to train visitors to collect scat. COVID has caused the training to switch from in-person to a soon-to-be posted video.
Several hikers have already helped provide information about the newest wolverines to the park.
“It was really beyond my expectation,” Chestnut said. “I was optimistic that if wolverines were present that we would detect them. But I definitely was not expecting to see babies, that’s for sure. And that we got reports from park visitors was also really exciting.”
Related Stories:

Conservation Groups Vow Challenge After Federal Decision Not To Protect Wolverines
Conservation groups are vowing to again challenge the U.S. Fish and Wildlife’s decision not to add wolverines to the Endangered Species List. There are likely fewer than 300 wolverines across its habitat across the Mountain West, which includes populations in Washington, Idaho and Oregon, where 90 percent of their habitat is on federally managed lands and wilderness areas.

Where Have All The Wolverines Gone? Apparently Not On The Endangered Species List (Yet)
Conservation groups say the animals need to be listed as threatened under the Endangered Species Act. Ten groups want to force the federal government to protect the elusive wolverines. The groups estimate there are around 300 wolverines left, sparsely scattered across the Mountain West, including Idaho, Washington and Oregon.
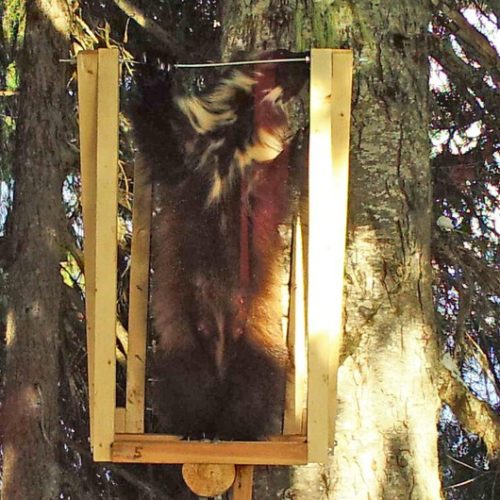

Rare Find: Wolverine Mother In Washington’s South Cascades
For the first time in recent history, a mother wolverine has been spotted in the southern part of Washington’s Cascade Mountains. The carnivores had been wiped out of the region after excessive hunting and trapping in the mid-1900s.