Old Growth Could Be Key For Native Songbird Species To Beat Climate-Change Heat
Listen
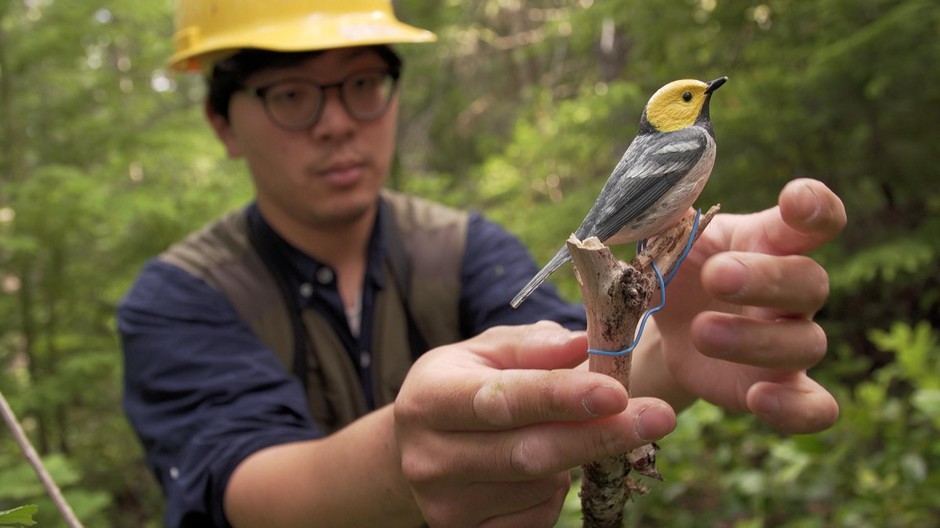
Hankyu Kim has gotten inside the head of the hermit warbler. He knows what makes the tiny songbird tick.
“These birds are territorial in the breeding ground, they set up their territories and they fight with each other to defend it,” he said.
Armed with this knowledge, a nearly invisible net strung between two repurposed fishing poles, a life-like plastic warbler decoy and a looping bird-call recording, the Oregon State University researcher’s trap is set.
Kim’s yellow hardhat matches the yellow head of the hermit warbler, which on cue, flies down from the upper canopy of the trees to investigate the source of the song. Kim hides in the bushes, trying to follow the frantic bird with binoculars.
“When birds fly in, they hit the net and drop down into a pocket and lie down there like a hammock,” Kim said.
And within just a few minutes the hermit warbler takes the bait, flying across a small clearing and hitting the net.
It’s another win for the decoy.
Heating Up
Kim and his colleagues are developing a new experiment in the Oregon Cascades to track the movements of hermit warblers through the forest. Learning how they move could help explain how bird species are dealing with rising temperatures and climate change.
“We have these long-term population monitoring routes across the Northwest. And a surprising number of species are declining,” said OSU professor Matt Betts. “Actually, more than about half of the species that live in a forest like this are in decline.”
Rising temperatures can shrink where some birds can live, and where they can find food.
For the hermit warbler, those declines are up to 4 percent each year.
Research by OSU’s Betts and Sarah Frey found warblers declined in areas with young forests, including those replanted after clear cut logging. But hermit warblers are doing better in other areas.
“In landscapes that had more older forest, their population declines were lowered, or even reversed, even though the climate has been warming,” Frey said.
The warblers thrived in areas with old growth — the forests seem to somehow shield them from the ill effects of rising temperatures.
The question now: “Why?” And this is where this new study comes in.
Following The Clues
Kim and fellow OSU researcher Adam Hadley moved the trapped hermit warbler’s feathers aside and attached a tiny radio tag to its back using non-toxic glue. Then they released the bird and it flew away unharmed.
Hankyu Kim uses a radio transmitter to track the movement of a tagged hermit warbler as it moves through a tree plantation at the HJ Andrews Experimental Forest. Learning how the small song birds travel over the course of a day could provide insight into why bird populations are doing well in old growth forests while declining in other warming landscapes of the Pacific Northwest. CREDIT: KERIN SHARMA
The next day was the true test. Hadley and the others pushed into a dense stand of trees, armed with receivers that look like old-fashioned TV antennas.
“It’s going away from us,” Hadley said, holding the antenna over his head.
“We’ll try to be as quiet as we can,” said Betts as branches snapped underfoot.
They walked down a drainage though a 50-year old tree plantation, a remnant of the H.J. Andrews Experimental Forest’s logging past. Then they crossed into a grove of much older trees – closer to 300 years.
“Given the differences in temperature across the whole height of the tree, it’s possible that when it’s warmer, they may be only using the bottom and more shady parts of the trees,” Hadley said.
The complex layers and sheer biomass of old growth keeps the temperature low.
“Versus in the cooler parts of the day, maybe they’re using all the way to the top,” he said.
But the researchers can’t fully know what’s going on without knowing more about how the birds use the forests. Hadley waved the antenna through the air trying to pinpoint the warbler’s location.
“I’m not getting the strongest signal at the top of the tree, seems to be a bit stronger in the mid-canopy,” he called out to Betts in the distance.
It became clear that tracking a tagged warbler on foot was possible. They’re able to tell roughly where it’s moving, both horizontally and vertically through the canopy.
Betts declared the trial run a success.
Down the road, if the researchers are able to track the hermit warblers through these forests, they’ll get another step closer to understanding how climate change is affecting native species. It’s clear that rising temperatures are going to be a factor going forward.
“I don’t see it likely that hermit warblers will have air conditioning any time soon,” Betts said.
But he adds that the Pacific Northwest might be in a better position than other regions to handle the changes ahead, because of the work we’ve already put in preserving our old growth forests.
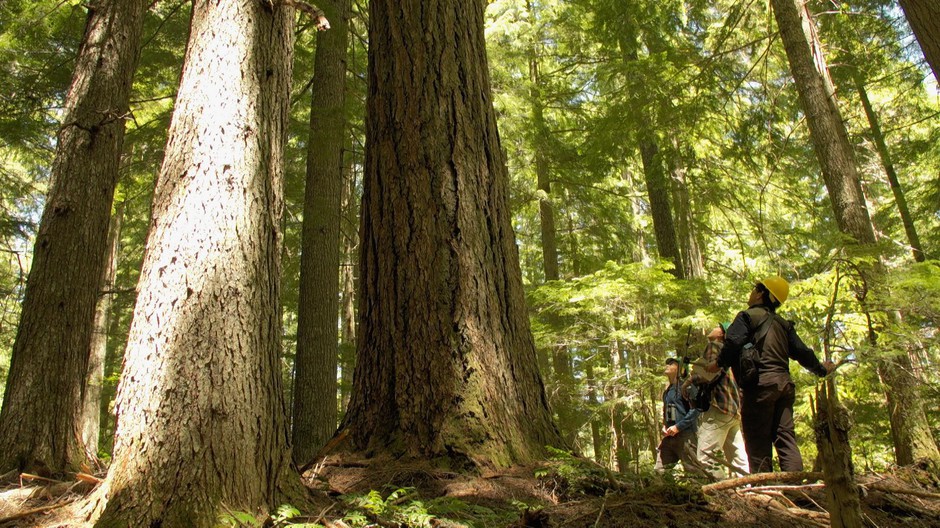

OSU scientists detect a tagged hermit warbler in the canopy of an old growth grove in the Oregon Cascades. Learning how the small song birds travel over the course of a day could provide insight into why bird populations are doing well in old growth forests while declining in other warming landscapes of the Pacific Northwest. CREDIT: GREG DAVIS
Related Stories:

Thousands of salmon eggs arrive at southeast Washington schools
Sarah Moffitt, education coordinator for Tri-State Steelheaders, pours salmon eggs into a tank at Davis Elementary School. (Credit: Susan Shain / NWPB) Listen (Runtime :59) Read It’s “egg day” at

This transfer will help Grand Coulee Dam run more efficiently, save money
One of the electrical switchyards at Grand Coulee Dam. (Credit: Bureau of Reclamation) Listen (Runtime 0:56) Read There’s a transfer happening at Grand Coulee Dam. After years of planning, the

To help cool the Tri-Cities, kids plant hundreds of trees for cooler parks, playgrounds
Elena Woodford and Alexis Nicholson help plant one of seven trees at Tapteal Elementary School. Alexis co-founded the Kids for Urban Trees club to plant trees in the community. (Credit: